We are experts in the use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning for processing Earth Observation data. We use these techniques for a wide range of image and video processing; for example, to detect objects, categorise them and recognise changes.
What is AI and Machine Learning?
Artificial intelligence refers to the use of computers to simulate the way humans learn and solve problems, using mathematical models. It adds the speed and scale of computing to the intuition and flexibility of human thinking.
Machine learning is a subset of AI. It refers to the process of using mathematical models to help a computer learn without direct instruction.
While Artificial Intelligence is the act of a computer thinking like a human and working unaided, machine learning is a means by which it develops its intelligence.
How does AI and Machine Learning help with Earth Observation?
At its simplest, AI and Machine Learning helps us with a range of visual processing, such as detecting and categorising objects, and recognising changes.
Applying Artificial Intelligence to Earth Observation allows high performance data processing and decision making at a scale that would not be possible with human or traditional computing approaches.
It allows us to handle more data sources, process data more quickly, increasing the scale and sophistication of data analysis while reducing the cost to clients.
Example Earth-i offerings using AI and Machine Learning
Intelligence as a service (INTaaS)
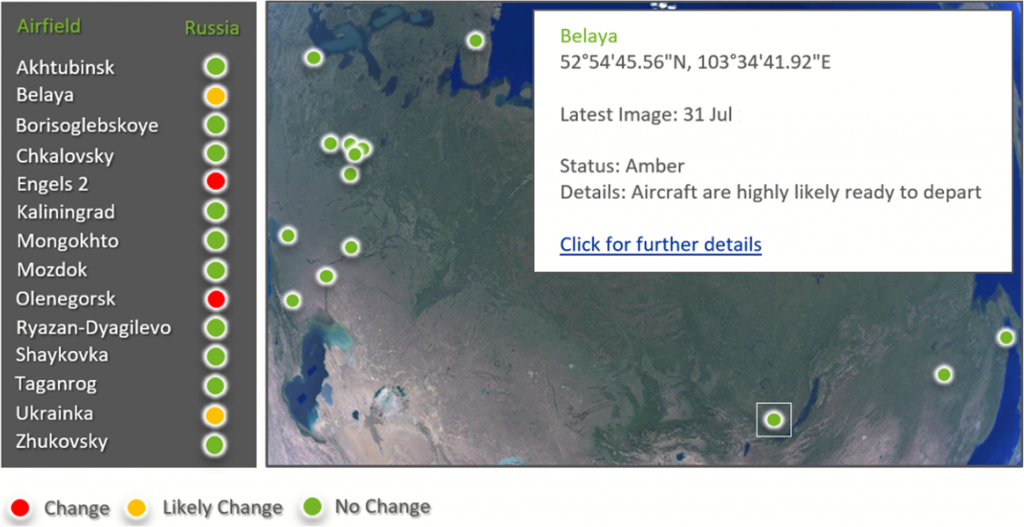
We apply machine learning and artificial intelligence techniques to commercially available imagery to facilitate the understanding of assets and their states of readiness. Specific equipment types can be identified by type and location through automated image analysis.

Monitoring an area of interest with satellite imagery allows a normal pattern of life to be built up through frequent image collection and analysis. This can then be used to identify abnormal behaviours which could indicate emerging threats or potential crises.
Automatic Infrastructure Identification from Satellite
Current infrastructure vulnerability mapping relies on multiple data sources together with intensive manual effort. By capturing the skills of manual image interpretation into algorithms, satellite data can be analysed in minutes to detect most important infrastructure assets, to hugely reduce the time taken to map these locations in emergencies or otherwise. The data can then be passed to others for further interpretation.
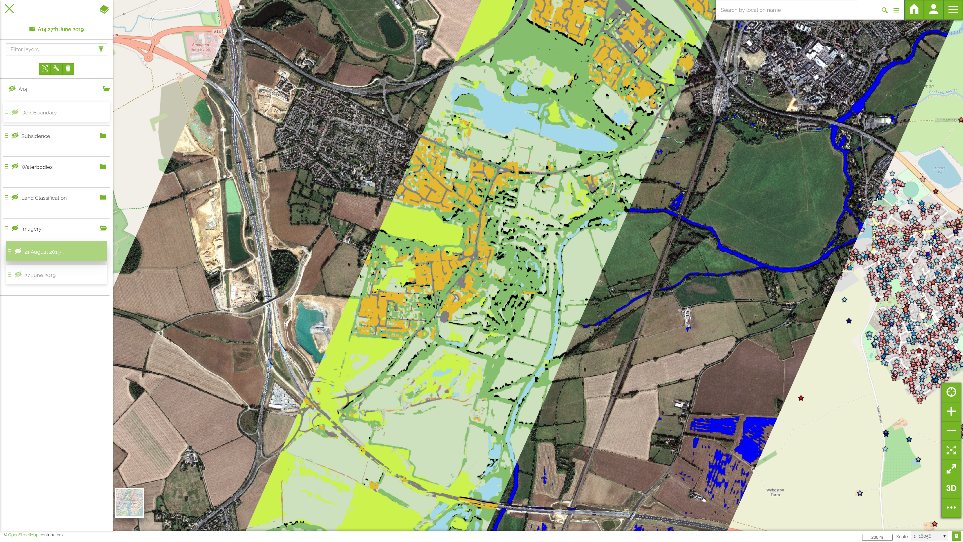
| For example, given an image such as this: | |
| It takes seconds to pull out key features of roads: | |
| And buildings: | |
| In order to create a complete infrastructure map that can be monitored over time for changes. |