Earth Observation enhances agriculture
In agriculture, Earth Observation imagery and data analytics have revolutionised food production and supply chain management with the development of precision farming.
Precision agriculture enhances farmers’ understanding of how to get the best from their land by combining geographical, remote sensing and real-time data which will lead to making better decisions, improving crop yields and reducing production costs.
Soil condition and crop health monitoring across huge areas
Data from satellites provides a snapshot of a huge area of farmland in one image. The information within that image can be used to monitor changes in soil conditions and crop health, detect the presence of diseases or the effects of pests and be used to plan the most efficient future use of land whilst ensuring compliance with regulations.
How does it work?
Satellites that can ‘see’ in both visible and infra-red can map the presence of healthy, green vegetation. This information is presented as a number called the Normalised Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) and variations in that value will provide information as to amount of crop coverage and the health of that crop (as dehydrated or sickly crops reflect less infra-red light).
Why is it important?
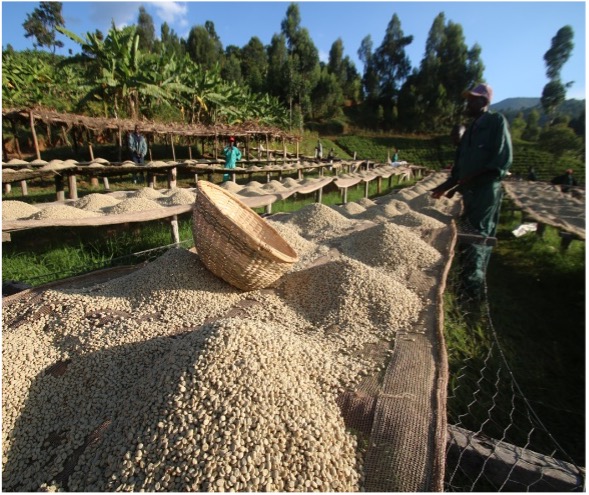
Food security for a rapidly increasing population is critical, and the use of precision agriculture has transformed farming. But much as agriculture is now big business, small farmers and farms, often in developing countries, are just as critical to world food markets and to the health of their local economies.
Earth Observation can offer precision agriculture companies access to timely and detailed geospatial information that can assist agricultural guidance systems to manage crop production and maximise yields in large-scale farming enterprises or provide critical decision-support to small-holder farms in developing countries.
Detailed geospatial intelligence over wide areas with high frequency revisits enables effective decision-support. When integrated with other data sources, such as predictive models for weather and pests, geospatial analytics and intelligence are combatting the impact of climate change and working towards more sustainable global food supply.
Sample Applications:
- Mapping agricultural land and crop classification
- Vegetation and crop health monitoring
Terrain feature identification and change monitoring - Site-specific crop yield management programmes
- Climate change mitigation