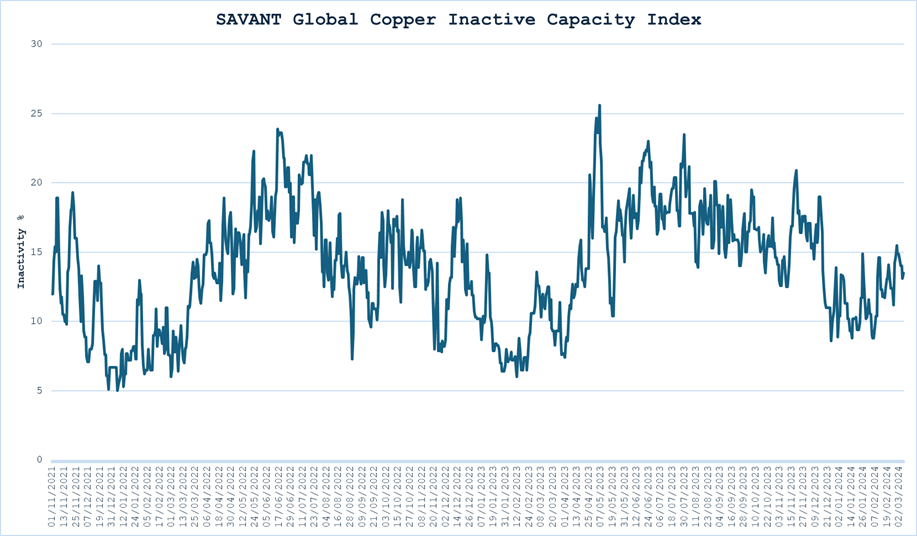
12 March 2024 – London – Latest data from Earth-i‘s SAVANT real-time global copper monitoring index, shows that an average of 11.5% of copper smelter capacity monitored (90% of the global total) was inactive in the first two months of the year, compared with a more typical 8.6% in the same period last year and 8% in January-February 2022. In top producer China, inactive capacity averaged 8.3% this year compared with 4.8% in the comparable period last year.
Production in China is normally elevated during this period, as regular maintenance closures tend to take place later in the year. Copper market watchers are tracking Chinese output carefully at the moment, not only because it is the world’s biggest producer, but also because it is the main destination for mined concentrate and a hub for custom smelters, treating third party material.
Certainly, copper treatment charges (a key source of custom smelter income) are historically low. Price Reporting Agency Fastmarkets reported that its copper concentrate treatment charge (TC) index, launched in March 2015, fell to its lowest level on record of $12.70/tonne at the start of this month, down from $48.20/tonne at the beginning of the year and just above $70/tonne a year ago.
Since the start of 2024, or even slightly before the end of 2023, SAVANT notes that the Baotou and Kunming smelters in China have shown up as inactive, while the Wuxin facility has displayed as inactive since last summer. Partly offsetting this, Northern Copper’s revamped Houma smelter started activity last October and appears to have been operating on a consistent basis since. At present, it would not take much for smelter activity to return to more usual levels. But the market is mindful of comments earlier this year by China’s Copper Smelter Purchase Team, which represents the country’s major producers, that production cuts might be in the offing. This now seems more likely with a meeting scheduled for this week.
Outside China, there have been no real surprises. “We picked up minor outages in mid-February at Australia’s Olympic Dam and Chile’s Chuquicamata and continue to monitor Adani’s new Kutch smelter in India, which is expected to start activity shortly,” said Richard Blain, Founder & Director of Earth-i.
One thing is certain, global copper mine production growth will be muted this year after the cuts to guidance announced by major producers in recent months, especially coming on top of the suspension of First Quantum’s sizeable Panama operation.
And while refined copper supply depends also on production from solvent extraction-electro-winning (SX-EW) operations at mine sites, concentrate tightness looks set to peg back smelter activity this year, with a knock-on effect on cathode output.
“With global copper mine supply tight and raw material processing charges at depressed levels, timely updates on smelter activity are essential for an early steer on the outlook for copper production and its potential impact on this year’s refined market balance,” concluded Blain.
The Inactive Capacity Index is derived from binary observations of a smelter’s operational status as being either active or inactive. The capacity weighted global and regional indices show the percentage of smelter capacity that is inactive, with readings displayed in the chart below as a weekly rolling average. A reading of zero would indicate 100% smelting capacity.
The SAVANT platform monitors up to 90% of the smelting capacity for copper, nickel and steel around the globe. Using daily updated sources, including extensive use of geospatial data collected from satellites, the index reports on the activities at the world’s smelting plants offering subscribers unprecedented levels of coverage, accuracy and reliability. This dataset allows users to make better informed and more timely trading decisions.
Sign-up here for a trial of the SAVANT service.
About Earth-i
Earth-i is a geospatial intelligence company using machine learning, artificial intelligence and Earth Observation data to provide unique and relevant insights, derived from diverse geospatial data, that deliver clear decision advantage for businesses, governments and other organisations.
Earth-i provides advanced analytics using automated interpretation of a range of geospatial Earth Observation data sources including colour imagery, colour video, infra-red and radar from a range of sources including satellite, drone, aerial and ground-based sensors. This data is fused with additional data sources to extract factual understanding and generate predictive insights across a range of markets such as commodities, supply chain, agriculture, infrastructure and defence.
For more information visit:
Website: www.earthi.space / LinkedIn: Earth-i







