12 March 2025 – London – Global copper smelting activity fell for the first time since October last year according to Earth-i’s SAVANT’s Global Copper Monitoring Index. Average smelting activity decreased by 0.2%* in February, as deduced from a rise in the global inactive capacity index from 8.6% in January to 8.8%. Nevertheless, smelting activity remains strong, defying prevailing market conditions for treatment and refining charges, or ‘TC/RCs’, with February’s figure still the second highest reading in the last two years.
TThe fall in activity in the global index was notable as this came despite continued strength in China, where the country level inactive capacity index fell for the fourth consecutive month to only 5.5%, the lowest average figure since March 2023. While this is consistent with seasonal patterns and the uptick in economic activity that comes with the spring thaw in the northern hemisphere, it is nonetheless remarkable given TC/RCs at record lows for the annual benchmark and spot market terms that are now widely marked in negative territory by the industry’s price reporting agencies (PRAs).
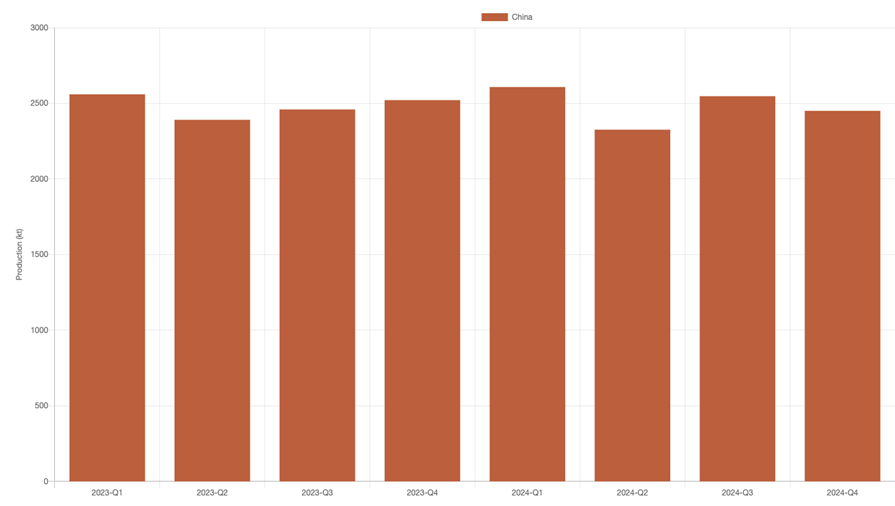
Indeed, by the first week of March, there were no major smelters in the country that SAVANT monitoring showed were undertaking any maintenance downtime. However, our China production series in beta did register a 3% y/y fall in output in Q4, indicating that some plants are likely to be operating at lower utilisation rates and/or processing lower grade concentrates to try and reduce variable and working capital costs (see Figure 1).
Fig I: SAVANT China quarterly production series (in beta), Q1 2023 – Present
Meanwhile, smelting activity in the Rest of World fell by 1.6%, as deduced by a rise in the inactivity series from 9.9% in January to 11.5% in February. The largest increase across the regions was seen in Europe, where inactivity climbed 4.5% to 7.4%. This was despite there appearing to be no major maintenance stoppages, with a week-long outage at KGHM’s 140 kT/a Legnica smelter in the middle of the month being the most significant observation.
Other regions to record rises were Asia & Oceania (+3% to 3.0%) and Africa (+0.6% to 24.9%). Concurrently, in the Americas smelting activity increased with North America recording a gain of 4.8%, while South America saw a rise of 1%.
Fig II: Legnica smelter activity, December 2024 – Present
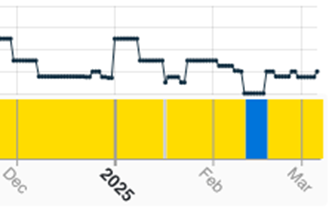
Yellow = Active / Blue = Inactive / Grey = No reading
From here it will be very interesting to see how the market reacts to news that the Indonesian government will reportedly grant a quota to PT Freeport Indonesia (PTFI) to once again allow the export of concentrates before the company’s new Manyar smelter achieves full ramp-up, which is not expected to be achieved until the end of this year. Concentrates from PTFI’s Grasberg mine typically go to smelters in Japan, Korea and India rather than China due to their high gold content and could provide these plants with something of a lifeline in the current market.
* – All figures are m/m unless otherwise stated
See more about Earth-i’s SAVANT Global Copper Monitoring Index here.
About SAVANT:
Earth-i’s SAVANT platform monitors up to 95% of the smelting capacity for copper and nickel around the globe and provides indicators of smelter activity and production around the globe, in an easy-to-understand format, covering multiple metals and minerals.
Data is collected and analysed using advanced algorithms derived from Computer Vision and Machine Learning techniques. Data is taken from several different Earth Observation satellites and our global and regional indices are updated at a high frequency to give consistent, insightful and dependable results.
Activity is scientifically measured using a consistent methodology. Over eight years of historical data is available.
About Earth-i:
Earth-i is a geospatial intelligence company using machine learning, artificial intelligence and Earth Observation data to provide unique and relevant insights, derived from diverse geospatial data, that deliver clear decision advantage for businesses, governments and other organisations.
Earth-i provides advanced analytics using automated interpretation of a range of geospatial Earth Observation data sources including colour imagery, colour video, infra-red and radar from a range of sources including satellite, drone, aerial and ground-based sensors. This data is fused with additional data sources to extract factual understanding and generate predictive insights across a range of markets such as commodities, supply chain, agriculture, infrastructure and defence.
For more information visit:
Email: savant@earthi.co.uk / Website: www.earthi.space / LinkedIn: Earth-i







