Earth-i, London 15 May 2025 – Global copper smelting activity fell by another 1.1% in April, although in a sign of how competition between operators has intensified, levels remain well above those last year. According to data from Earth-i’s SAVANT Global Copper Monitoring Index, global inactivity rose from 12.6% in March to a monthly average of 13.7% in April – the highest reading since November. However, the second quarter is typically a period when smelters undertake down time to conduct maintenance so that in April 2024 the series registered 17%, before rising to 19.2% in May.
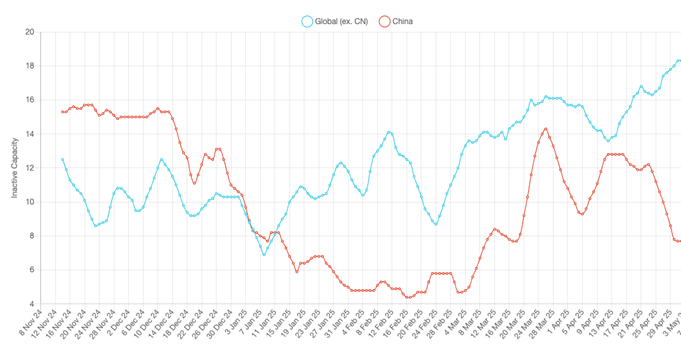
Not surprisingly, China continues to show much stronger activity than plants in the Rest of World, with the country level inactivity series registering only 10.8% for April, compared to 15.9% for smelters ex-China. This is a consequence of an economic model that is less responsive to prevailing market conditions as plants can run on very thin margins – or even makes losses – for extended periods of time, due to their value to the provincial economy in terms of employment and GDP. In these circumstances, it appears that many owners are waiting for others to blink first.
Additionally, as we highlighted in our feature article Copper smelting’s new paradigm, smelters employing traditional operating models are under increasing pressure from modern plants in new jurisdictions being commissioned for their strategic value.
Fig I: China and RoW inactive capacity, November 2024 – Present
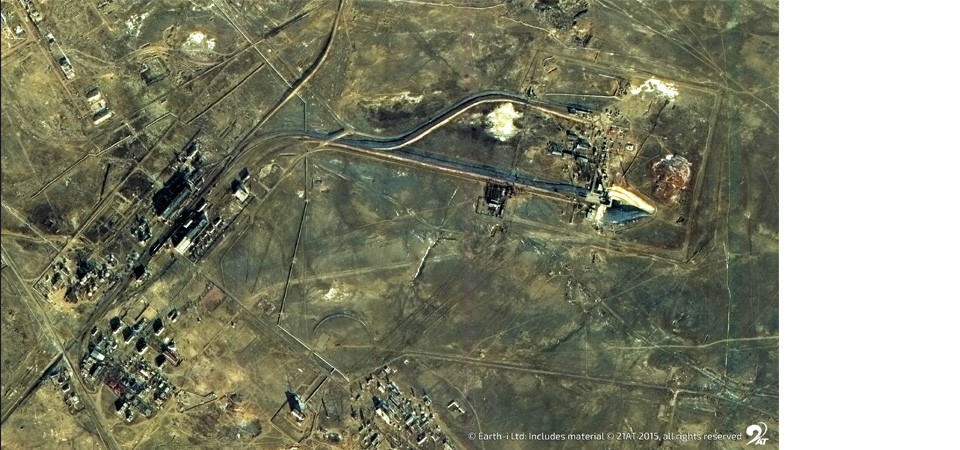
Of the regions, Africa saw the largest fall in activity with the Mother Continent’s inactivity index rising by 9.6% to 34.1%, while the same series for South America increasing by 4.6% to 32.5%. The smelters most responsible for these gains were Sinomine’s 60 kT/a Tsumeb in Namibia and Glencore’s 310 kT/a Altonorte plant in Chile’s Antofagasta region. Interestingly, despite media reports that the latter could remain out of action for an extended period following the declaration of force majeure in March, SAVANT monitoring shows heat signatures for May 5th and 6th, indicating that the facility looks to have returned to production. AT 32.5%, North America is the other region with an inactivity reading greater than 30%.
Elsewhere, activity increased in Europe by 5.8% so that the continent now has the lowest inactivity reading of all the regions at only 4.4%, surpassing Asia & Oceania where inactivity rose by 3.2% to 6.1%.
Fig II: Altonorte smelter ‘hotspots’, May 2025

* all figures are m/m unless otherwise stated
For more information:
Email: savant@earthi.co.uk / Website: www.earthi.space / LinkedIn: Earth-i
About SAVANT:
Earth-i’s SAVANT platform monitors up to 95% of the smelting capacity for copper and nickel around the globe and provides indicators of smelter activity and production around the globe, in an easy-to-understand format, covering multiple metals and minerals.
Data is collected and analysed using advanced algorithms derived from Computer Vision and Machine Learning techniques. Data is taken from several different Earth Observation satellites and our global and regional indices are updated at a high frequency to give consistent, insightful and dependable results.
Activity is scientifically measured using a consistent methodology. Over eight years of historical data is available.
About Earth-i:
Earth-i is a geospatial intelligence company using machine learning, artificial intelligence and Earth Observation data to provide unique and relevant insights, derived from diverse geospatial data, that deliver clear decision advantage for businesses, governments and other organisations.
Earth-i provides advanced analytics using automated interpretation of a range of geospatial Earth Observation data sources including colour imagery, colour video, infra-red and radar from a range of sources including satellite, drone, aerial and ground-based sensors. This data is fused with additional data sources to extract factual understanding and generate predictive insights across a range of markets such as commodities, supply chain, agriculture, infrastructure and defence.







