15 January 2025 – London – Following November’s 2.7%* rise, copper smelting activity registered another gain in December, this time of 1.9%, according to Earth-i’s SAVANT’s Global Copper Monitoring Index. The collective 4.6% increase in smelting activity over the last two months (as deduced by a fall in inactivity from 16.1% in October to 11.5% in December) is the largest since January 2024 and before that February 2023, reflecting the consistent seasonal pattern driven by the timing of Chinese New Year.
1.9% rise, driven by surprise jump in China and record highs in Asia & Oceania
However, this year with operators having to contend with falling treatment and refining charges, or ‘TC/RCs’, from already very low levels that prompted calls from the China Smelter Purchasing Team (CSPT) for production cuts and maintenance extensions, it was surprising that smelting inactivity in China fell by 2.0% to 13.2%. Nonetheless, with inactivity in Rest of World also shedding 1.7% to 10.4%, the peculiarity we noted last month of activity being stronger ex. China is testament to these market pressures for smelters on the mainland, where over three quarters of country-level operating capacity is classified as ‘custom’, so that they purchase their concentrates from third parties.
Fig I: Inactivity at smelters in China and Rest of World, Jul – Dec 2024
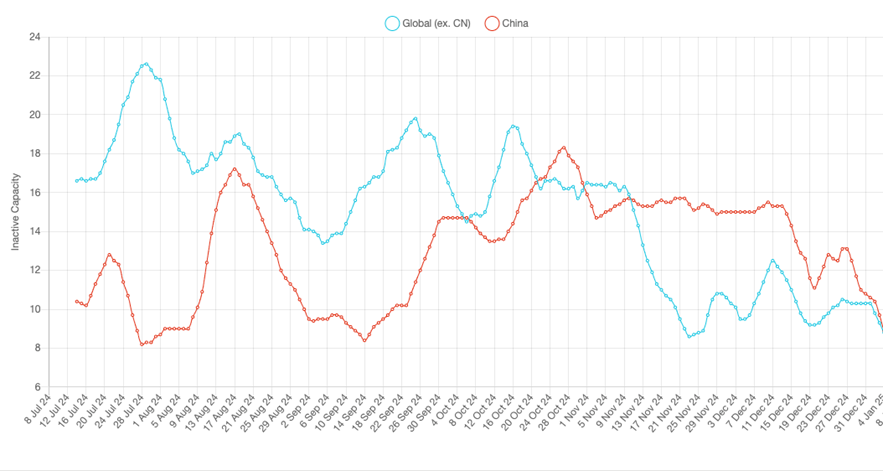
Indeed, smelting activity increased in all regions except for South America for the second consecutive month, with the largest gain made in North America, where the regional inactivity index fell by over 17 points to 13.9%, its lowest reading since April 2020. This was in large part due to strong performances at Freeport McMoRan’s 180 kT/a Miami as well as Rio Tinto’s 320 kT/a Garfield.
North America was not alone in seeing smelting activity at multi-year highs in December, with Africa recording the highest monthly average for activity since March 2022, despite the breakdown of the oxygen plant at Mopani Copper Mines’ 320 kT/a Mufulira site that is expected to keep the smelter offline until the end of February. Meanwhile, Asia & Oceania registered the highest monthly average on record since SAVANT monitoring began in 2016.
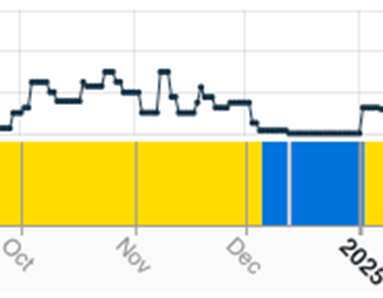
At a country level, activity in Chile was notable for a sharp rise in inactivity that contributed to the regional index jumping from 16.5% to 34%, primarily due to what appears to have been a ~25-day stoppage at Codelco’s 450 kT/a Chuquicamata. The increasing dependence of Chilean cathode production on this smelter as well as the 400 kT/a El Teniente plant, is one of the reasons we believe the government is looking for partners to build a new facility on the site of the dormant 80 kT/a Hernan Videla Lira smelter in Paipote, Atacama, a vanguard of the re-shoring trend we noted in our most recent feature article, Copper smelting’s new paradigm.
* all figures are m/m unless otherwise stated
Fig II: Mufulira smelter activity, Q4 2024
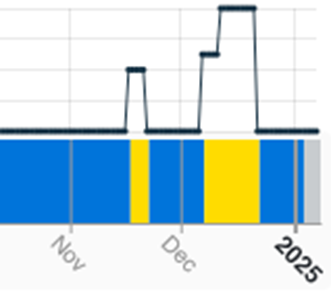
Fig III: Miami smelter activity, Q4 2024
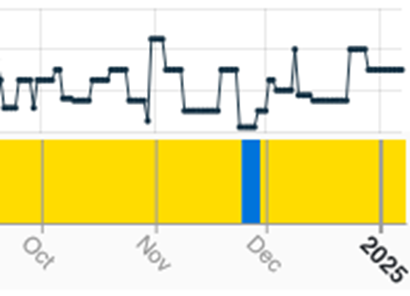
Fig IV: Chuquicamata smelter activity, Q4 2024
Yellow = Active / Blue = Inactive / Grey = No reading
See more about Earth-i’s SAVANT Global Copper Monitoring Index here.
About SAVANT:
Earth-i’s SAVANT platform monitors up to 95% of the smelting capacity for copper and nickel around the globe and provides indicators of smelter activity and production around the globe, in an easy-to-understand format, covering multiple metals and minerals.
Data is collected and analysed using advanced algorithms derived from Computer Vision and Machine Learning techniques. Data is taken from several different Earth Observation satellites and our global and regional indices are updated at a high frequency to give consistent, insightful and dependable results.
Activity is scientifically measured using a consistent methodology. Over eight years of historical data is available.
About Earth-i:
Earth-i is a geospatial intelligence company using machine learning, artificial intelligence and Earth Observation data to provide unique and relevant insights, derived from diverse geospatial data, that deliver clear decision advantage for businesses, governments and other organisations.
Earth-i provides advanced analytics using automated interpretation of a range of geospatial Earth Observation data sources including colour imagery, colour video, infra-red and radar from a range of sources including satellite, drone, aerial and ground-based sensors. This data is fused with additional data sources to extract factual understanding and generate predictive insights across a range of markets such as commodities, supply chain, agriculture, infrastructure and defence.
For more information visit:
Email: savant@earthi.co.uk / Website: www.earthi.space / LinkedIn: Earth-i







