12 February 2025 – London – Global smelting activity rose for the third month running in January, accelerating by 3.0%*, according to Earth-i’s SAVANT’s Global Copper Monitoring Index as smelter inactivity averaged only 8.6%, the lowest figure since February 2023. Indeed, the fall of 7.5% since October 2024 is the largest 3 month decline in 4 years.
The driving force behind this surge in activity came from smelters in China, where the country level inactivity index fell by 6.5% to just 6.7%, the lowest reading since March 2023. As we pointed out last month, this is consistent with seasonal patterns driven by the timing of Chinese New Year, as well as the requirement to have product ready for semi fabricators to take advantage of the uptick in economic activity that comes with the end of winter in the northern hemisphere. As we hypothesised in our latest feature article, Cat Theory and The Great Copper Conspiracy, it would seem that operators on the mainland have taken the collective position that they are more able than their competitors to ride out an extended period of low treatment and refining charges, or ‘TC/RCs’, which have fallen sharply again in recent weeks. And not only are existing smelters like Daye’s 400 kT/a Hongsheng Copper coming back online, but new facilities are ramping up, with Yunnan Copper’s 200 kT/a Kunming 2 and Jinchuan’s 300 kT/a Gansu no.2 being the most prominent, which SAVANT monitoring shows have started commissioning since October and November respectively.
Fig I: Smelting activity, selected Chinese smelters, Q4 2024 – Present
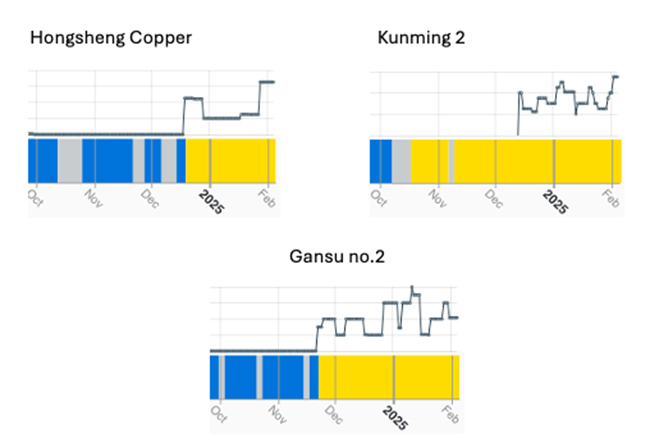
Yellow = Active / Blue = Inactive / Grey = No reading
Smelting inactivity in Rest of World also declined, but by only 0.5% to give an average inactivity reading of 9.9% for January, again the lowest reading in almost 2 years. At a regional level, activity in Asia & Oceania rose for the third consecutive month, while that in Europe rose for the fourth month in a row. Interestingly, the 3.7% rise in regional smelting activity in the latter was primarily the result of strong activity signals from the larger smelters in the region, especially Aurubis’ 360 kT/a Pirdop in Bulgaria. This would seem to build on the strong Q4 2024 operating result which saw the smelter produce 57 kT of copper cathodes during the period, as work progresses with the expansion of the tankhouse that will increase capacity at the site by around 50% to 340 kT/a.
Fig II: Pirdop smelter activity, Q4 2024 – Present
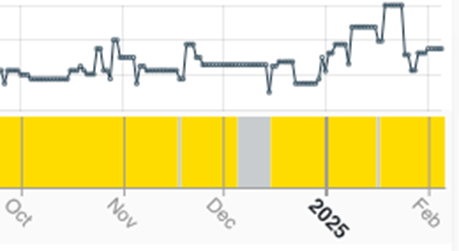
Yellow = Active / Blue = Inactive / Grey = No reading
Activity in South America also increased with the regional inactivity index falling from an average of 34% in December to 25.2% in January.
The only two regions where inactivity rose during the month were Africa and North America, by 8.7% and 12.4% respectively, although as we noted in our January release, these came off a base of smelting activity at multi-year highs.
Fig III: Inactivity at smelters in Africa and North America, Feb 2024 – Present
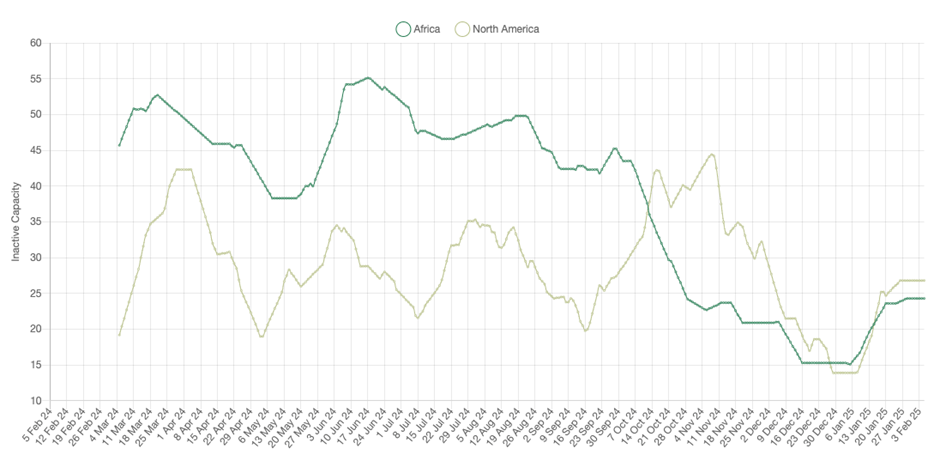
* – All figures are m/m unless otherwise stated
See more about Earth-i’s SAVANT Global Copper Monitoring Index here.
About SAVANT:
Earth-i’s SAVANT platform monitors up to 95% of the smelting capacity for copper and nickel around the globe and provides indicators of smelter activity and production around the globe, in an easy-to-understand format, covering multiple metals and minerals.
Data is collected and analysed using advanced algorithms derived from Computer Vision and Machine Learning techniques. Data is taken from several different Earth Observation satellites and our global and regional indices are updated at a high frequency to give consistent, insightful and dependable results.
Activity is scientifically measured using a consistent methodology. Over eight years of historical data is available.
About Earth-i:
Earth-i is a geospatial intelligence company using machine learning, artificial intelligence and Earth Observation data to provide unique and relevant insights, derived from diverse geospatial data, that deliver clear decision advantage for businesses, governments and other organisations.
Earth-i provides advanced analytics using automated interpretation of a range of geospatial Earth Observation data sources including colour imagery, colour video, infra-red and radar from a range of sources including satellite, drone, aerial and ground-based sensors. This data is fused with additional data sources to extract factual understanding and generate predictive insights across a range of markets such as commodities, supply chain, agriculture, infrastructure and defence.
For more information visit:
Email: savant@earthi.co.uk / Website: www.earthi.space / LinkedIn: Earth-i







