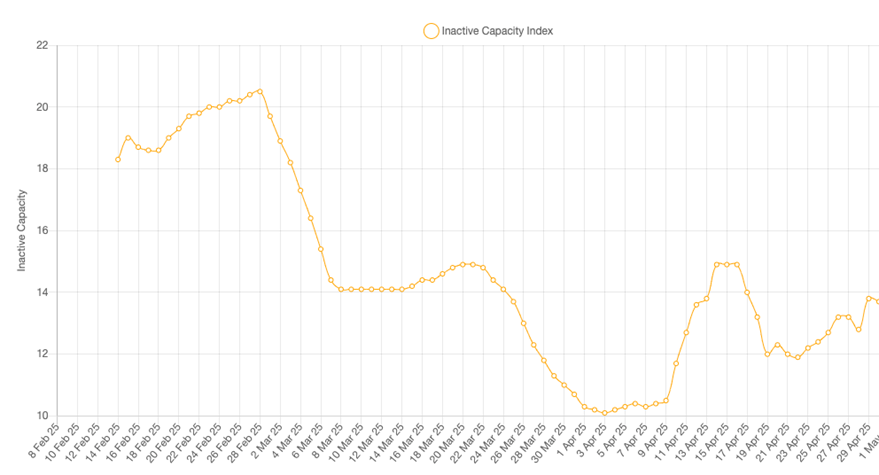
Earth-i, London 13 May 2025 – Global nickel smelting activity increased by 0.8% in April, driven by another strong performance from Indonesia. According to data from Earth-i’s SAVANT Global Nickel Monitoring Index, inactivity in the Southeast Asian nation that accounts for 58% of SAVANT nickel capacity coverage, fell by 0.7% to an average of just 6.9%. This helped pull the Global Inactive Capacity Index down to 12.6% for the month, 9.4% below the same period a year ago, supporting the hypothesis of the International Nickel Study Group (INSG) that in 2025 the nickel market is heading for a surplus exceeding 5% of the total market size for a third year running.
Fig I: Global Inactive Capacity Index, February 2025 – Present
Of the other regions, only in China did inactivity increase, by 3.2% to 18.9%. This is unsurprising as the industry continues to transition away from nickel pig iron (NPI) following the ban of nickel ore exports from Indonesia in 2020. Despite a rise in imports of ore from the Philippines, SAVANT monitoring indicates that as many as 15 NPI producing sites in China have been shuttered since the beginning of the decade. That inactivity at a country level is not higher is due to growing capacity of nickel matte and/or nickel cathodes
With China and Indonesia dominating global production, inactivity in other regions has been at elevated levels for some time. This is most obvious in Europe, where the regional inactive capacity series registered its fourteenth consecutive reading above 50%, despite falling 9.3% to 54.3%. The growth of the NPI industry in the 2010s and the subsequent fall in nickel prices has, together with ageing plants and relatively high electricity costs, rendered much of the region’s ferronickel smelting capacity uncompetitive. Add to this the war in Ukraine that has seen production at Solway Investment Group’s 22 kT/a Pobuzhskiy plant halted and SAVANT monitoring indicates that there has been no ferronickel production on the continent since at least the start of 2024, save for a short period of activity at Yildirim Group’s 12 kT/a NewCo Ferronikeli plant in Kosovo in early February and mid-April last year.
Meanwhile activity in all other regions also rose. In Africa, the Mother Continent’s inactive capacity series fell by 20.8% to 22.2%, in the Americas by 1.4% to 28.6% and in Asia & Oceania by 4.8% to 7%.
Fig II: NewCo Ferronikeli smelter activity, January 2024 – Present
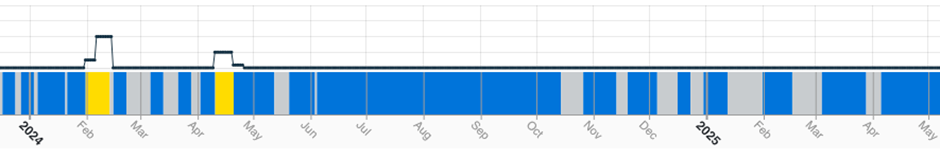
Yellow = Active / Blue = Inactive / Grey = No reading
* all figures are m/m unless otherwise stated
For more information:
Email: savant@earthi.co.uk / Website: www.earthi.space / LinkedIn: Earth-i
About SAVANT:
Earth-i’s SAVANT platform monitors up to 95% of the smelting capacity for copper and nickel around the globe and provides indicators of smelter activity and production around the globe, in an easy-to-understand format, covering multiple metals and minerals.
Data is collected and analysed using advanced algorithms derived from Computer Vision and Machine Learning techniques. Data is taken from several different Earth Observation satellites and our global and regional indices are updated at a high frequency to give consistent, insightful and dependable results.
Activity is scientifically measured using a consistent methodology. Over eight years of historical data is available.
About Earth-i:
Earth-i is a geospatial intelligence company using machine learning, artificial intelligence and Earth Observation data to provide unique and relevant insights, derived from diverse geospatial data, that deliver clear decision advantage for businesses, governments and other organisations.
Earth-i provides advanced analytics using automated interpretation of a range of geospatial Earth Observation data sources including colour imagery, colour video, infra-red and radar from a range of sources including satellite, drone, aerial and ground-based sensors. This data is fused with additional data sources to extract factual understanding and generate predictive insights across a range of markets such as commodities, supply chain, agriculture, infrastructure and defence.







